
A hacksaw is a fine-toothed saw, originally and mainly made for cutting metal. Hacksaws use thin blades to cut metal and plastics and other materials that can’t be cut with ordinary saws.
For example, you can use one to cut bolts that are too long or saw through a PVC plastic pipe easily. Most hacksaws are hand saws with a C-shaped walking frame that holds a blade under tension.
Use the Right Hacksaw Blade
Blades are rated in TPI, or Teeth Per Inch, each of which is suited for cutting different materials and thicknesses.
Hacksaw Blade General Applications
| Teeth Per Inch (TPI) | Suitable Hacksaw Blade Application |
| 14 TPI | Aluminum, Brass, Copper, soft metals. Thick and Soft Plastics. |
| 18 TPI | Aluminum, Brass, Copper, thick pieces of square-stock and round-stock Steel, round bar that is 1″ thick or more. Suitable for General Workshop Cutting (The Go-To Blade). |
| 24 TPI | Aluminum, Brass, Copper, Hard Plastics, Steel Angle-Iron up to ¼” thick, Steel Plate up ¼” (5-6mm). |
| 32 TPI | For Cutting Hollow Sections and Steel Tubing, Sheet Metal. |
Hacksaw Blade TPI Chart by Material and Workpiece Thickness
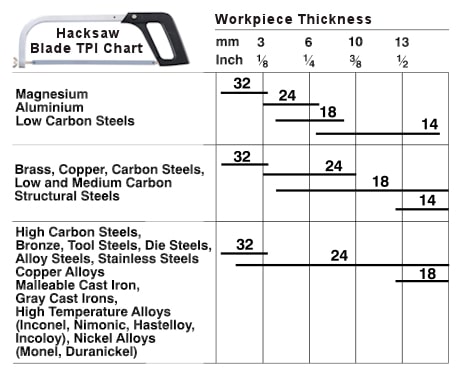
Making The Cut with a Hacksaw
Start your cut with light, short strokes. This will make a small notch that helps the saw settled into the cut without sliding left and right.
Once the blade begins to cut, gradually lengthen the stroke and push harder but only slightly — let the blade do the work.
Compact and Full-Size Metal Cutting Hacksaw Comparisons and Reviews
Catus Maximus reviews both Compact and full-size metal cutting hand hacksaws, including:
- Milwaukee 48-08-0320
- Stanley 15-113
- Sandvik 219 and Sandvik 268
Hacksaws and Blades
Browse more Hacksaws and Blades on Amazon…














