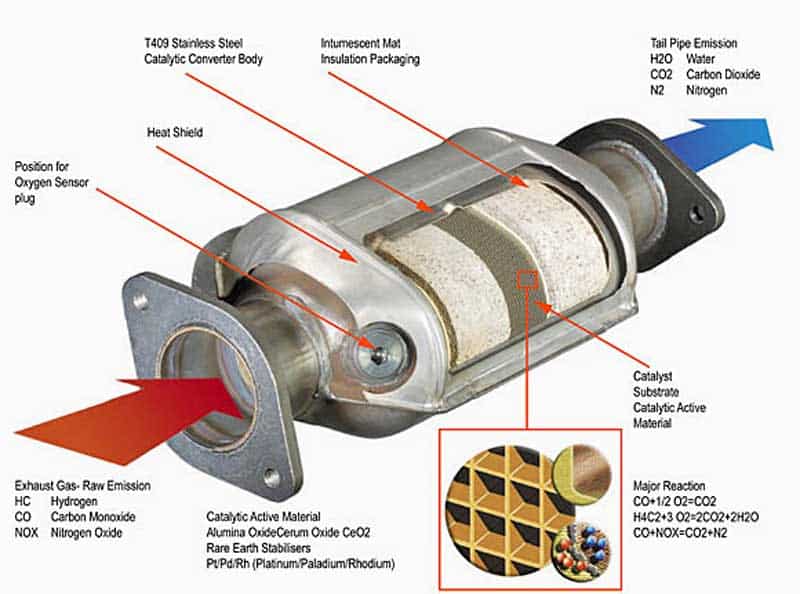
A catalytic converter is a component found in the exhaust system of a vehicle.
What the catalytic converter does is burn the carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons to create nitrogen.
It does this by using platinum and palladium/rhodium as catalysts, but at the same time, it reduces the nitrogen oxides. In other words, it separates the oxygen atom rather than adding it. This process will help reduce toxic tailpipe emissions and it helps reduce smog.
In the US in 1968 there were new rules about automobile emissions that were brought out and that is when catalytic converters suddenly became very popular in every state. Now they are in almost every vehicle around the world.
Catalytic converters cannot operate in the presence of lead. Therefore, their introduction would cause leaded gasoline to phase out. You will also find that catalytic converters are also common in industrial processes to reduce all the harmful emissions. But the most common place to find them is in automobiles.
The byproducts of an automobile engine are ideally only:
- Carbon dioxide
- Water
- Nitrogen (only some)
This is also similar to the chemical output of animals. In practice though, the combustion process in an engine is never 100% efficient as it leaves behind hot, yet unburned hydrocarbons.
Before the 1960s, they didn’t know that all these emissions were a public and an environmental health hazard.
Catalytic converters rapidly oxidize a very large percentage of the remaining unburned hydrocarbons, and this results in much cleaner emissions.
But, because the catalytic converter must operate at such a high speed to catch the unburned hydrocarbons before they fly out of the tailpipe, it will put a limit on how efficient the oxidation process can be.
Over the years vehicles have become cleaner and cleaner, and this is due to the increasing quality of catalytic converters. What is still difficult though is, the lowering of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions.
The reason for this is because carbon dioxide cannot be oxidized into anything less harmful. It is a known greenhouse gas and it contributes to global warming.
Catalytic converters in automobiles seem to operate at quite a high temperature, normally around 750 degrees F or around 400 degrees C. Where catalytic converters in the industry can often be dozens of times larger than those in automobiles and also so much hotter.
There are some standard components of catalytic converters, and they are:
- A line burner
- Catalytic bed — this is usually in the form of either ceramic honeycombs or ceramic beads covered in the catalyst.
- Heat exchanger